Ransomware in 2024: The Threat to Business Resilience
Ransomware has become one of the biggest cybersecurity threats for today's business environment. We analyze the impact, statistics, and ISO/IEC 27001-based prevention strategies.
Ransomware has become one of the biggest cybersecurity threats for today’s business environment, where business continuity is crucial for success and competitiveness. The increasing sophistication of cybercriminal tactics, including the use of artificial intelligence, makes these attacks increasingly difficult to prevent and mitigate.
To confront this threat, it is essential that companies adopt proactive measures and robust prevention and recovery strategies. This includes implementing advanced backup and recovery solutions, as well as constant employee training in security practices. Additionally, adherence to international information security standards such as ISO/IEC 27001 plays a crucial role in protecting data and organizational resilience against ransomware attacks.
Ransomware Impact on Businesses
Ransomware has been a formidable threat to organizations of all sizes and sectors in 2024. This type of malware can not only paralyze daily operations but also cause catastrophic financial and reputational damage.
“Ransomware remains a matter of ‘when’ rather than ‘if’.” - Veeam, Data Protection Trends 2024 Report
Most Affected Sectors
Ransomware affects businesses across all sectors. Financial services organizations, for example, were impacted by 65% in 2024, remaining in line with the 64% reported in 2023 (Sophos). Other highly affected sectors include healthcare, education, and government, due to their critical technological infrastructures which, in many cases, lack appropriate security measures.
Financial Impact
In 2024, average costs to recover an affected company rose to $2.73 million, representing a significant increase compared to the $1.82 million recorded in 2023 (Sophos). This increase reflects both direct recovery expenses and indirect losses, including business interruption and revenue loss.
Operational Disruption
Ransomware attacks cause significant disruptions to a company’s daily operations. According to Sophos data, on average, 49% of an organization’s devices are affected during an attack. Although it is uncommon for an organization to experience total encryption of its environment, even a partial disruption can result in prolonged downtime and significant productivity losses.
 Figure 1. Operational disruption due to a ransomware attack
Figure 1. Operational disruption due to a ransomware attack
Veeam’s 2024 ransomware trends report reveals that ransomware remains the primary cause of IT operations disruptions, with 41% of production data affected during an attack. Additionally, only 57% of compromised data can be recovered, leaving organizations vulnerable to significant data loss and negative business impact.
Reputation and Trust
Beyond financial costs and operational disruption, ransomware attacks have a lasting impact on a company’s reputation. Customer trust can erode if the company is perceived as lacking adequate cybersecurity measures. Likewise, data breaches can result in legal and regulatory consequences, further aggravating the harm to the company.
“Too many companies neglect a critical factor that insurance cannot solve: reputational damage.” - Jeffrey Ton, Forbes Councils Member
Business Continuity
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
To protect organizations from the devastating impact of ransomware, it is crucial to implement a combination of technical measures, security policies, and staff training. Below are key strategies, all aligned with the ISO/IEC 27001 standard, that can help prevent ransomware attacks and mitigate their consequences.
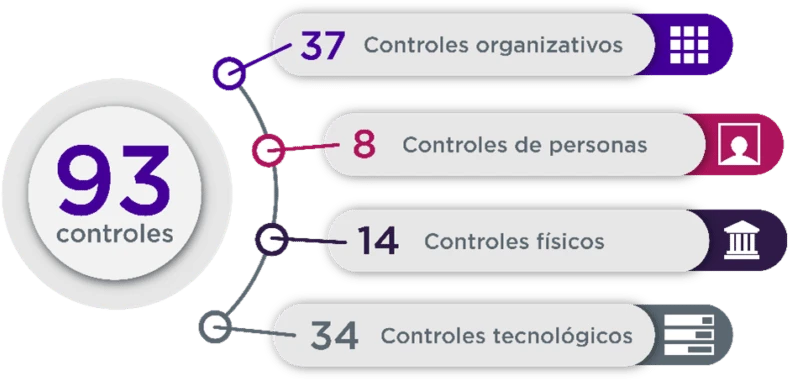 Figure 2. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Controls
Figure 2. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Controls
Structure Your Company’s Security
Organizational Controls (A 5.1-5.37) focus on how the organization addresses data security, from implemented policies and processes to organizational structure.
- Information security policies: Develop and maintain clear and effective policies covering all aspects of cybersecurity, ensuring data protection and business continuity. For example, encourage the use of strong passwords and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts.
- Organizational structure: Designate security officers and create security committees to oversee and continuously improve information security practices.
Keep Your Staff Prepared
People Controls (A 6.1-6.8) define how staff interact with data and information systems, as well as their security training.
81.3% of organizations offer end-user training on how to recognize and prevent ransomware attacks, highlighting the importance of employee preparedness and awareness (Hornetsecurity Q3 2024). This approach is crucial, given that social engineering and phishing continue to be predominant attack methods.
- Continuous training programs: Implement continuous training programs for all employees, focusing on identifying and preventing phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics.
- Phishing simulations: Conduct periodic phishing attack simulations to assess staff preparedness and response.
- Background checks: Conduct employee background checks to minimize the risk of insider threats.
“Ransomware is more about manipulating vulnerabilities in human psychology than about the technological sophistication of the adversary” - James Scott, Institute for Critical Infrastructure Technology
Protect Your Offices and Devices
Physical Controls (A 7.1-7.13) ensure the protection of physical information assets and technological infrastructure against unauthorized access and natural disasters.
- Clean desk policy: Implement a clean desk policy to prevent sensitive information from being exposed to unauthorized persons.
- Security and access systems: Control access to sensitive areas through entry and restricted access systems.
Use Technology to Your Advantage
ISO/IEC 27001 Technological Controls (A 8.1-8.34) are essential for maintaining a secure and compliant IT infrastructure. Implementing these technical solutions can help prevent and mitigate ransomware attacks.
- Advanced security software: Use cybersecurity solutions that include threat detection and response, firewalls, and behavior analysis.
- Regular updates: Keep all systems and software updated with the latest security patches.
- Backups: Perform frequent backups and ensure they are immutable, protecting them against malicious alterations or deletions.
- Cryptography: Develop a robust encryption management policy, protecting data in transit and at rest.
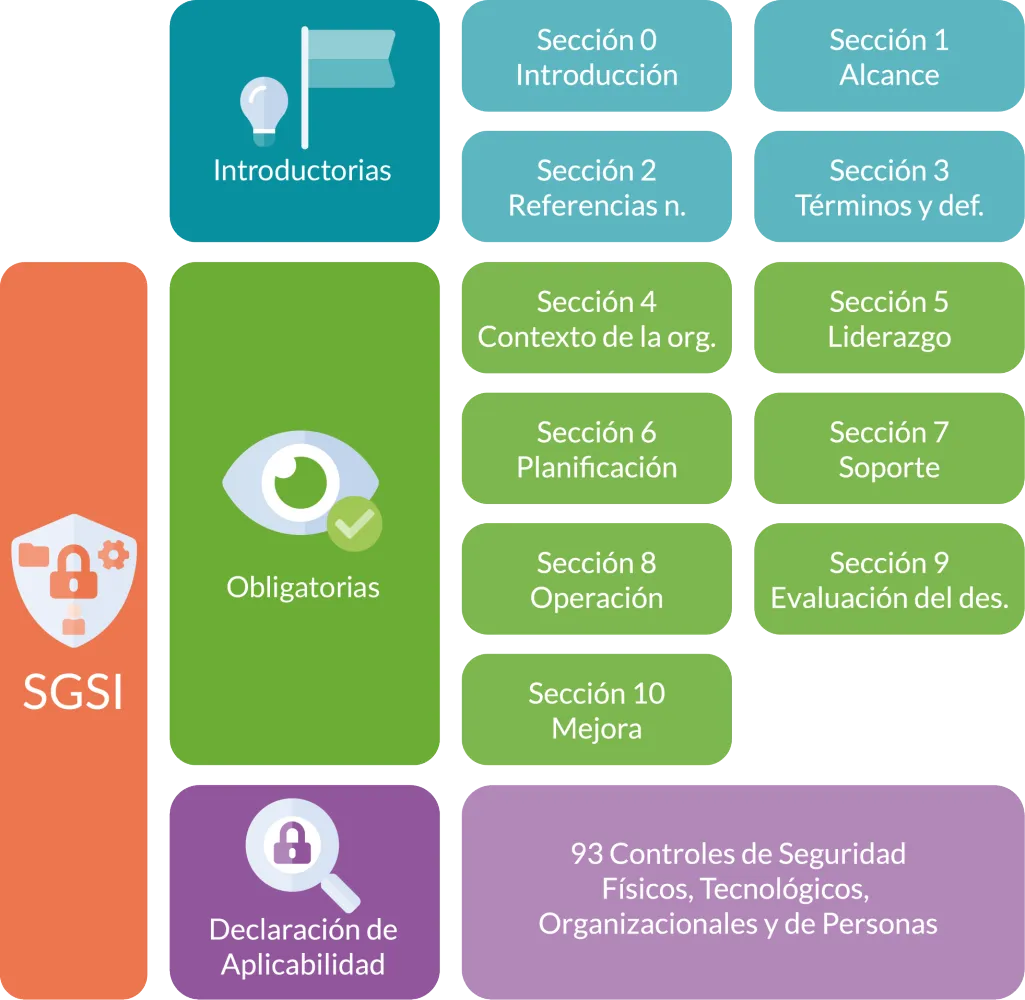 Figure 3. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Standard Structure
Figure 3. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Standard Structure
Business Cybersecurity Predictions
Ransomware remains one of the biggest cybersecurity threats for businesses, causing financial harm, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. Implementing a comprehensive approach based on the ISO/IEC 27001 standard is crucial to mitigate these risks and ensure business continuity.
In the coming years, an increase in the use of artificial intelligence by attackers to develop more sophisticated tactics is expected. In response, cybersecurity as a service is experiencing significant annual growth, providing companies access to advanced technologies and experts without the need to manage them internally. Additionally, cybersecurity regulations are intensifying each year, requiring organizations to adhere to stricter standards.
Regardless of sector or size, cybersecurity should not just be an option for businesses, but an urgent necessity and requirement. Staying informed and adapting to emerging trends is key to facing challenges and ensuring organizations are prepared to confront increasingly complex emerging threats.
Need to evaluate your organization’s security posture? Contact me for an initial consultation.